Research
Basic and need-driven materials science at the international forefront, empowering sustainable technologies with positive impact on society.
Materials Science for Sustainability
Materials are fundamental to modern society, providing the essential physical and structural framework for our advanced technologies and infrastructure. Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of research, involving the discovery, design, and characterization of innovative materials. It covers a wide array of materials, from solids such as alloys, ceramics, polymers, oxides, metals, and hybrids to fluids and molecular structures in gaseous states. Initially rooted in metallurgy, mineralogy, and ceramics, materials science has now evolved to include semiconductors, functional materials, biomaterials, heterostructures, and materials with reduced dimensionality among others.
Strategic framework
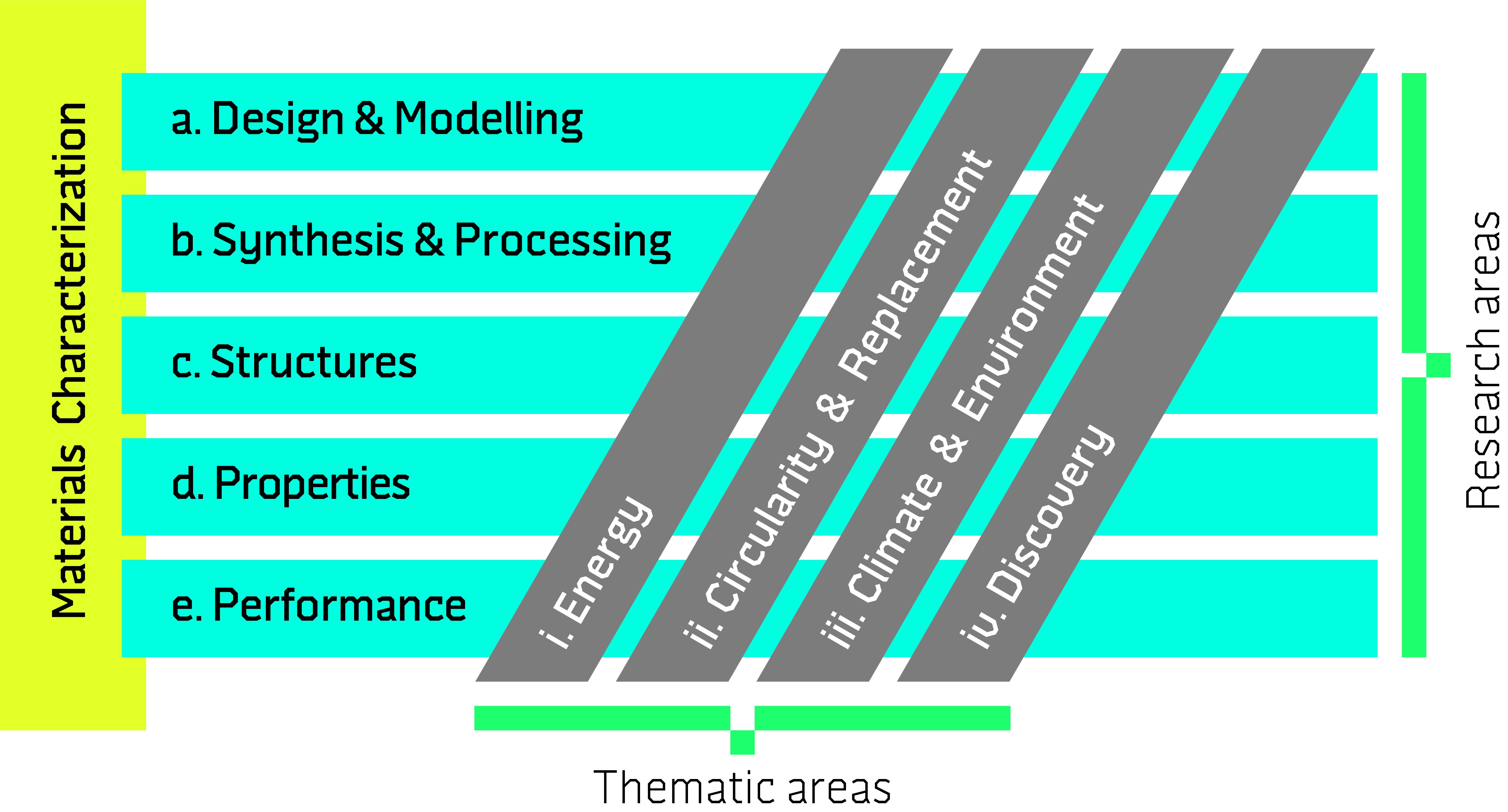
In recent decades, materials research has adopted a strategic framework built upon five pillars
- Design and modeling,
- synthesis and processing,
- structures,
- properties, and
- performance.
The essence of materials science lies in understanding the dynamic interplay among the structure of materials, their processing methods, and properties. Ultimately, this interplay determines the performance of a material for a given application. In line with sustainability goals, there is now a critical need to examine material flows from production to disposal, with a focus on minimizing process waste and energy consumption. This involves optimizing recycling, responsible mining, and eco-friendly production pathways.
As a response to these challenges, the WISE program addresses pressing scientific inquiries within materials science, concentrating on four key thematic areas.
Key thematic areas
Renewable energy sources
The utilization of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, requires harvesting and conversion into energy-rich carriers that can be readily used or efficiently stored and transported. Notably, hydrogen production via water electrolysis and fuels synthesized from CO2 is an example that presents significant materials challenges. Furthermore, addressing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources necessitates the development of effective energy storage solutions. This underscores the demand for low-cost materials with high energy storage capacities to be used in batteries and supercapacitors. Moreover, catalytically active materials for energy conversion and storage in chemical forms like hydrogen and redox-active molecules are very important.
However, many of the existing materials used in these applications include noble, rare, and non-sustainable elements limiting their global implementation. Therefore, there is a pressing need to explore sustainable alternatives. Recent advancements in functionalized, porous, and structured materials show promise, particularly in enabling the replacement of noble metals in fuel cell catalysts.
Finally, enhancing energy distribution and utilization efficiency is crucial. Using higher quality wide band-gap semiconductors can minimize losses in power conversion, while novel electronic materials can optimize electricity use in computing, data transfer, and appliances, thereby mitigating the escalating global electrical power consumption trend.
Materials and sustainability challenges
Many businesses rely on technologies that use materials presenting sustainability challenges. These include materials that involve critical or environmentally hazardous elements, or that are extracted under dubious mining conditions or causing negative environmental impact. There is an urgent need to focus on researching metals, ceramics, and other construction materials from a clean energy perspective. This means prioritizing materials constructed under CO2 neutral conditions, such as green steel.
Additionally, we need to explore bioplastics, materials from sustainable forestry, and lightweight composites. Examples of problematic materials include cobalt, used in hard metals and lithium-ion batteries, and rare-earth metals in wind turbine magnets, which face issues like controversial mining in the former case, and Chinese market dominance in the latter. Finding sustainable substitutions for such materials and developing efficient process for materials recycling are critical requirements for achieving sustainable development.
Environmental pollution
Human activities are the primary source of environmental pollution. In recent decades, materials science has offered solutions to reduce emissions of volatile organic compounds through conversion using catalytically active, nanostructured, and porous materials. Now, the world’s attention is turning towards strategies for capturing and converting CO2 to mitigate anthropogenic global warming.
Tailored materials for selective absorption and chemical conversion play a crucial role in such strategies, producing energy carriers like methanol or hydrogen from renewable sources. Progress has been made with photocatalysts and enzymatic conversion, but challenges persist, necessitating more efficient materials. Addressing point source emissions will require innovative materials, such as those for CO2 capture. Additionally, polluted sites on soil, at sea, or in the air demand further development of cleaning processes using materials optimized for specific pollutant separation or extraction. Looking ahead, replacing environmentally hazardous technologies will depend on discovering entirely new materials.
Significance of breakthrough research
While discoveries will be essential across all areas, our focus in this fourth thematic area is on emphasizing the significance of breakthrough research. Over the next fifty years, we anticipate the emergence of new technologies and applications driven by breakthrough discoveries of materials with unique and advanced performance properties. These discoveries will often arise unexpectedly from side-projects within larger programs, highlighting the importance of scientific freedom in pursuit of unforeseen materials. To foster this, we allocate 20% of the budget to high-risk, high-reward research with a sustainable perspective over a minimum of ten years.
Within our research framework of WISE, we envision exploration and advancement in several areas, including materials for energy-efficient information technology systems and high-tech devices, highly efficient solar cells, and the design of materials with inherent properties that facilitate their conversion into desired units, promoting a shift towards circular material flows. We aim to develop scalable processes for advanced functional materials to enable large-scale sustainable technologies, explore room-temperature superconductivity to address energy challenges, and push the boundaries of high-energy-density storage beyond current limitations.
Ever since the industrial revolution, catalysis has played a pivotal role in large-scale chemical production, driving affordability and enhancing living standards. Notably, the catalytic synthesis of ammonia for fertilizer production exemplifies its societal impact. Materials are integral to catalytic processes, enabling sustainable synthesis of both basic and fine chemicals, as well as future fuels aimed at sustainability.
These thematic areas intersect with the five pillars of materials science outlined above, forming the basis of the WISE matrix.